Guidance for Migrating VMware Virtual Machines to Amazon EC2
Summary: This implementation guide provides an overview of Guidance for Migrating VMware Virtual Machines to Amazon EC2. By following this implementation guide, you can use AWS Application Migration Service to migrate your virtual machines (VMs) to Amazon EC2, minimizing the cutover window and reducing potential impact or downtime to your customers.
Overview
In this implementation guide, we will walk you through the step-by-step process of completing VMware VM migrations to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) using AWS Application Migration Service. We will also show how to apply a custom post-launch action script to remove proprietary VMware tools from the migrated VMs.
Migrating on-premises VMware workloads to Amazon EC2 can provide significant benefits including increased scalability, improved performance, and reduced operational costs. Application Migration Service simplifies this process by providing a seamless, automated block-level replication solution for migrating VMware VMs to Amazon EC2 instances. Migrated VMs can be tested on Amazon EC2 while replication of the original source server continues. This Guidance uses the agent-based replication option as it provides continuous data replication and shortens the cutover window.
Architecture overview
This Guidance (Figure 1) follows the documentation, Network settings preparations for Application Migration Service by having a dedicated subnet for the service. It is used by the service as a staging area for data replication from your source servers. Test and cutover instances are launched in another dedicated subnet called Migrated Resources.
The AWS Replication Agents installed in the respective VMware VMs initiate the synchronization process, and data replication commences in the Staging Area. The replication is handled by replication servers based on the predefined replication settings. When the volumes attached to the source servers are replicated, the server is marked as: Ready for Testing. Regarding the launch settings, the respective test or cutover instances are launched in the Migrated Resources area.
This Guidance leverages Application Migration Service post-launch actions to install the AWS Systems Manager Agent (SSM Agent) on each test or cutover launched instances. The AWS SSM Agent allows the launch of custom scripts, such as removing the proprietary VMware tools.
This procedure is valid for both VMware Cloud on AWS and VMware on-premises.
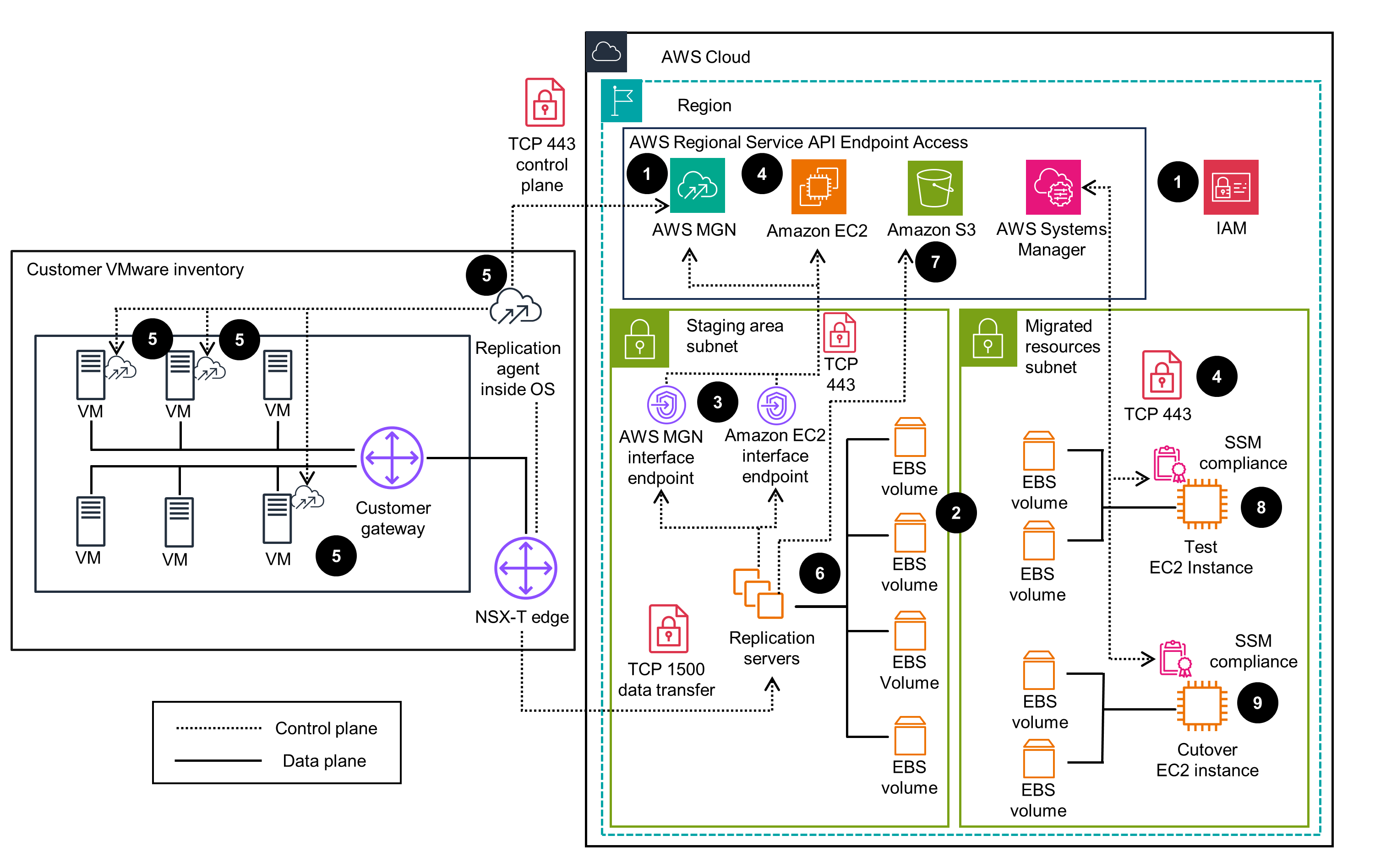
Figure 1: (Left) VMware environment with the AWS Replication Agents installed (Right) AWS account with its two subnets: Staging Area and Migrated Resources.
For demonstration purposes, this Guidance uses a Linux (RHEL 9) and Windows Server 2019 set of virtual machines.
Plan your deployment
Step 1 - Prerequisites
For this walkthrough, you will need:
An AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) user with required permissions, as defined in the Application Migration Service documentation: AWS Application Migration Service initialization and permissions.
Network settings as defined in: Network setting preparations.
A supported source server operating system. For more information about supported operating systems, review Supported operating systems.
Source VM credentials with permissions to download and install the AWS Replication Agent.
An Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) subnet that you will identify or create to use for your test and cutover instances along with the respective Amazon EC2 security groups.
Step 2 - Create Amazon VPC endpoints
The staging area and migrated area resources can run in a private or public subnet. In this scenario, both subnets are private. With no public access to any HTTPS endpoint, the launched instances cannot connect to the internet and therefore cannot execute the post-launch template. To allow installation of the SSM Agent and the execution of the post launch actions, three endpoint services need to be created:
com.amazonaws.<region>.ssm
com.amazonaws.<region>.ec2messages
com.amazonaws.<region>.ssmmessages
- For each endpoint that you need to create, open Amazon VPC in the console and select Endpoints, then select: Create Endpoint in the top right corner (Figure 2).
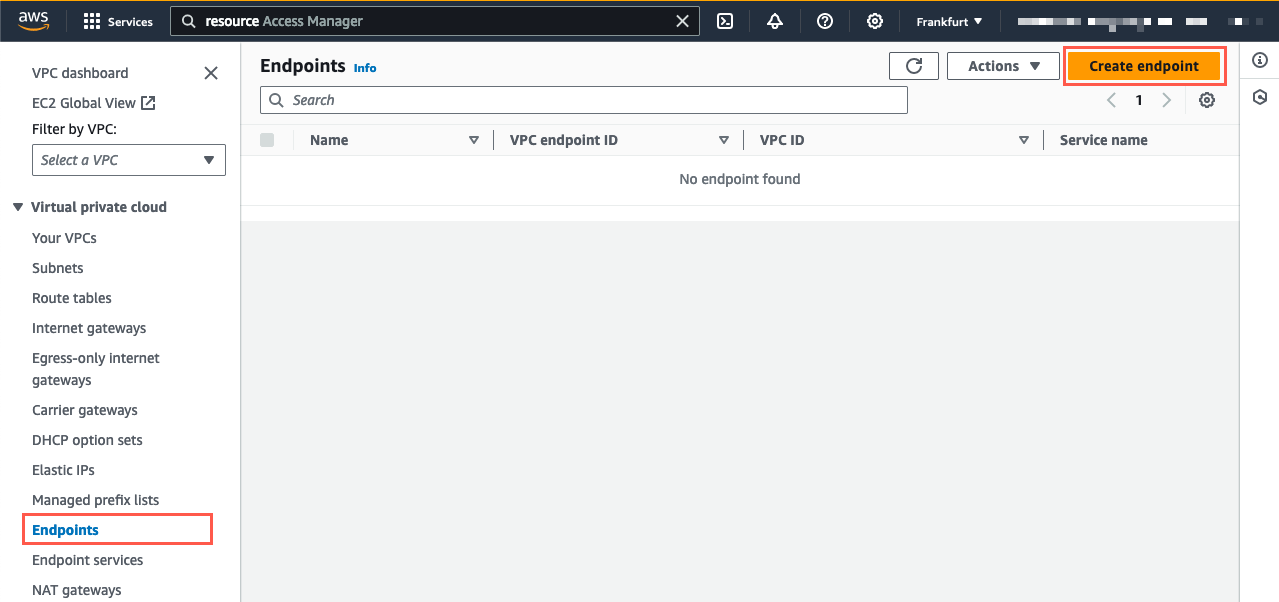
Figure 2: In the Endpoints section of the Amazon VPC service console, select Create endpoint.
Select AWS services and create the first endpoint (Figure 3) com.amazonaws.<region>.ssm. Replace <region> with the AWS Region where you utilize Application Migration Service. Select the target Amazon VPC and Amazon EC2 security groups. The security group attached to the VPC endpoint must allow incoming connections on port 443 from the private subnet of the managed instance. Finally, select Create Endpoint at the end of the page.
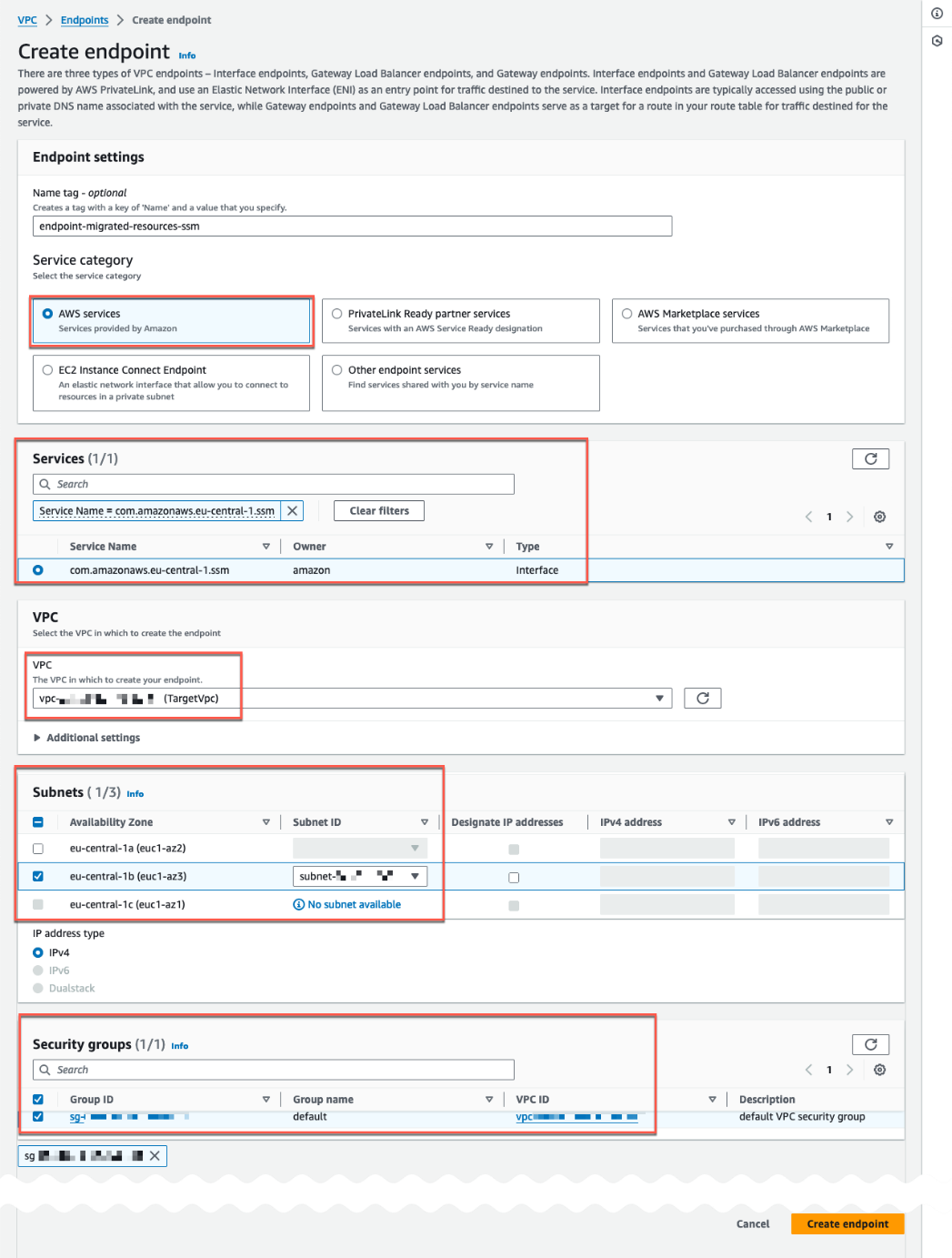
Figure 3: Create an endpoint from the Amazon VPC service console.
When the three VPC endpoints are created, you will see the following result shown in Figure 4.
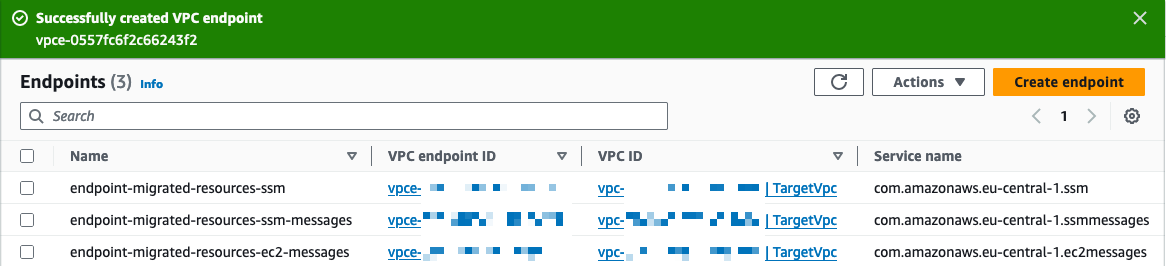
Figure 4: The three VPC endpoints are successfully created to allow the SSM Agent installation.
Step 3 - Post-launch actions to uninstall VMware Tools from Windows and Linux
This section introduces the creation of the custom post-launch settings to automate the removal of the VMware Tools after the source server has been launched in AWS. Note that changes to the post-launch templates will only be applied to newly added source servers. For existing source servers, you modify the post-launch template at the source server level.
- Access the template by selecting: Post-Launch template on the left-hand panel and Edit the post-launch actions settings (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Choose the Edit button to edit the template.
Activate the settings feature by toggling on Systems Manager agent installation on launched Test and cutover instances (recommended). Finally, select Save template (Figure 6).
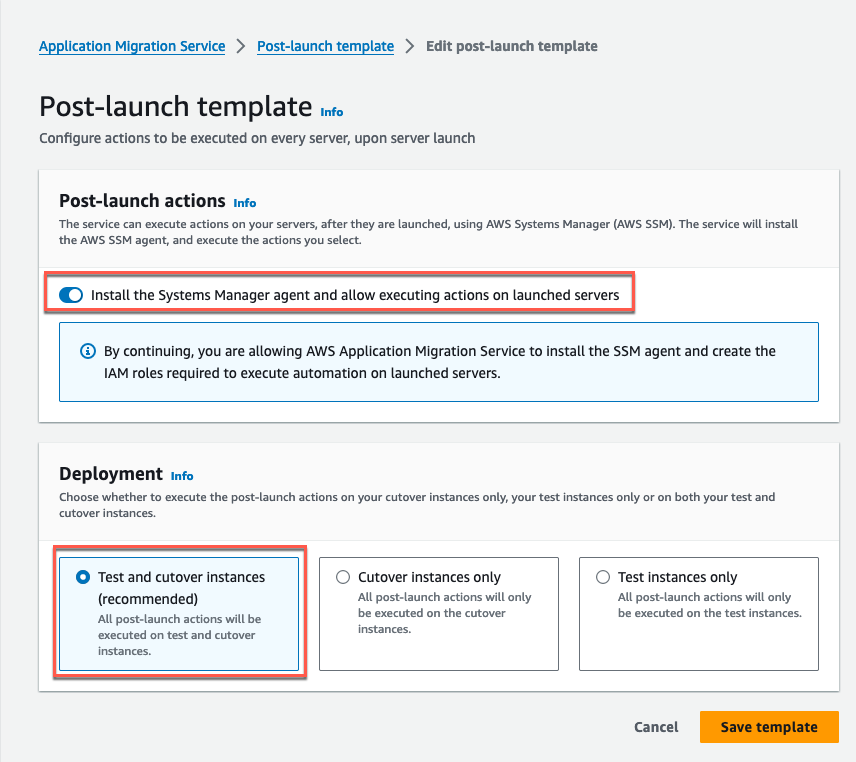
Figure 6: Enable SSM Agent installation for future test and cutover launched servers.
As a result, the template displays that the SSM agent installation is activated (Figure 7).
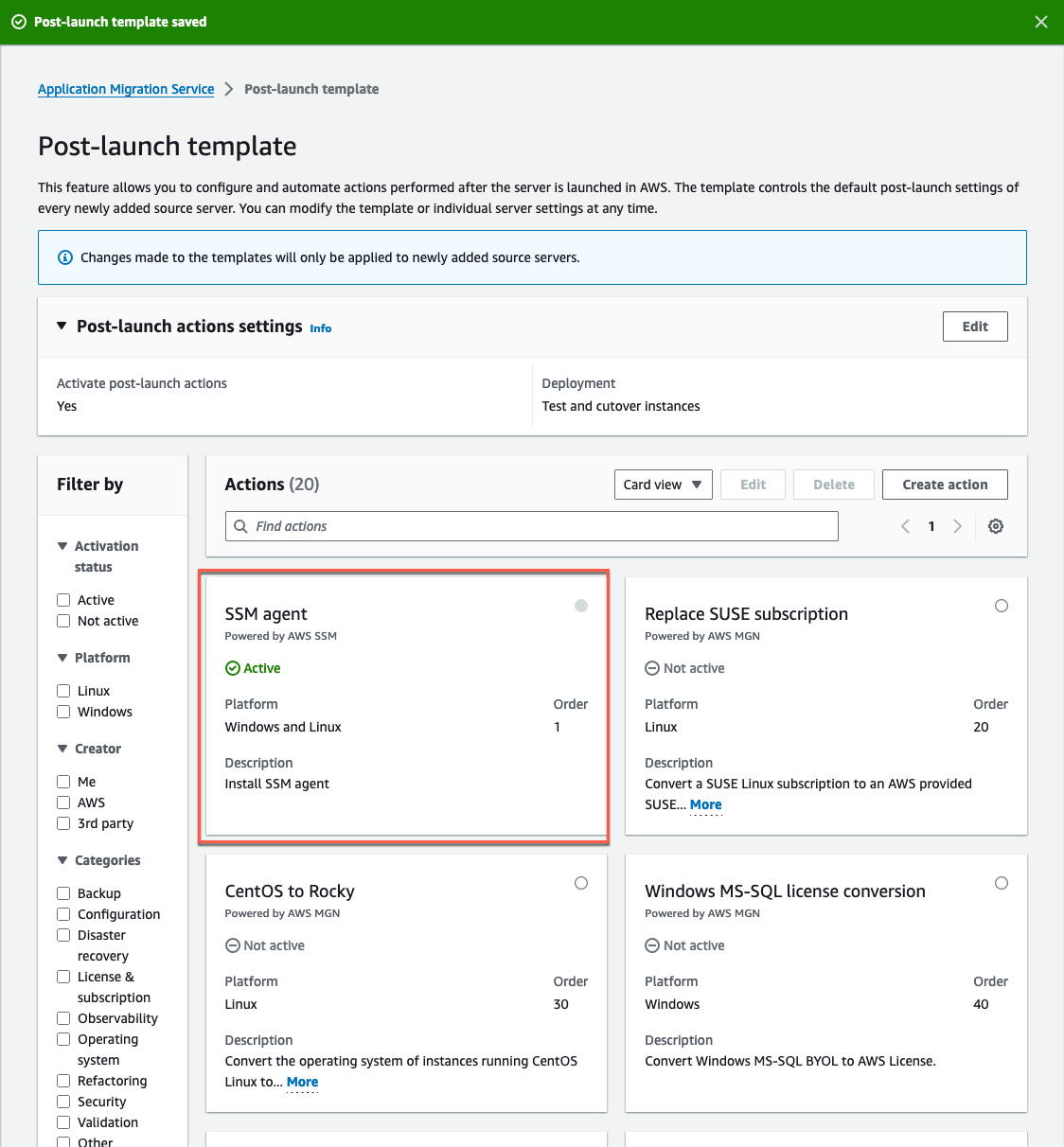
Figure 7: SSM Agent action is activated.
- To purge VMware images from VMware tools, start by creating a custom action. Select Create action (Figure 8).
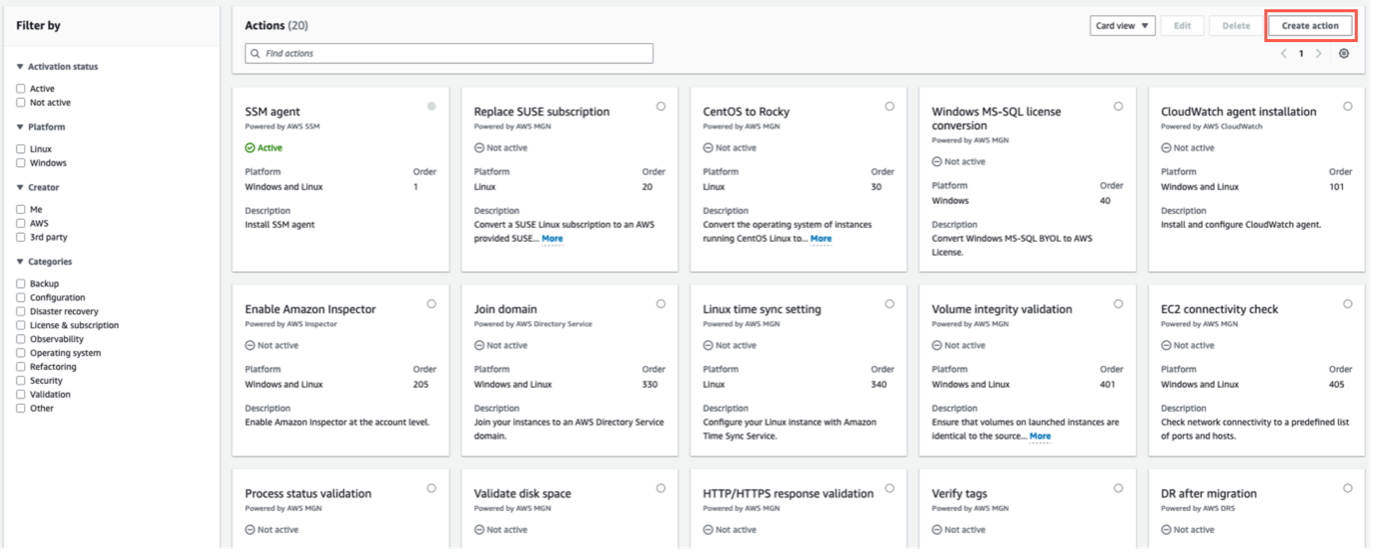
Figure 8: Select Create action on the top right corner.
Add the following input in the action settings (Figure 9).
- Windows script
Post-launch scripts on Windows run under the Local Service context.
Action name: CleanUpVMwareTools-Windows.
Select the option, Activate this action.
Systems Manager document name: AWS-RunPowerShellScript.
Description: Run a PowerShell script to clean Windows images from VMware tools.
Operating systems: Windows.
Action parameters:
The following script can be utilized to uninstall VMTools post migration from Windows Server 2019.
Commands:
<Remove-Item --path .\\VMware --recurse\ \$regpath = "HKLM:\\Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\uninstall"\ Get-childItem \$regpath \| % {\ \$keypath = \$\_.pschildname\ \$key = Get-Itemproperty \$regpath\\\$keypath\ if (\$key.DisplayName -match "VMware Tools") {\ \$VMwareToolsGUID = \$keypath\ }\ MsiExec.exe /x \$VMwareToolsGUID /qn /norestart\ }>workingDirectory: C:\Program Files\
executionTimeout: 300
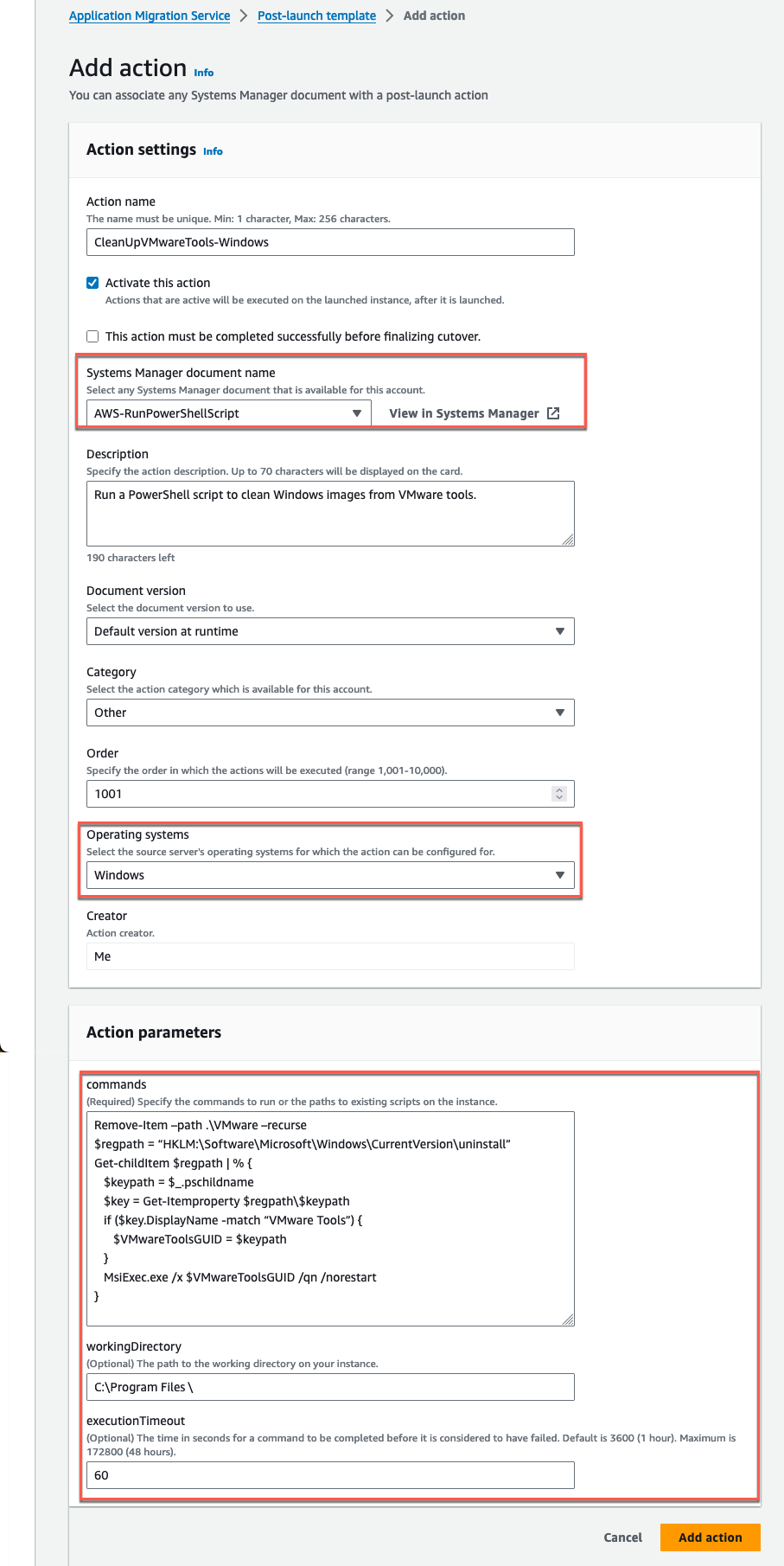
Figure 9: PowerShell script to remove VMware tools from replicated Windows launched instances.
- Repeat the above steps for the Linux instance (Figure 10). Post-launch scripts on Linux run under the root user. Refer to Uninstalling VMware Tools for other operating systems than RedHat Linux.
Action settings:
Action name: CleanUpVMwareTools-Linux.
Select the option, Activate this action.
Systems Manager document name: AWS-RunShellScript
Description: Run a Shell script to clean Linux images from VMware tools.
Operating systems: Linux.
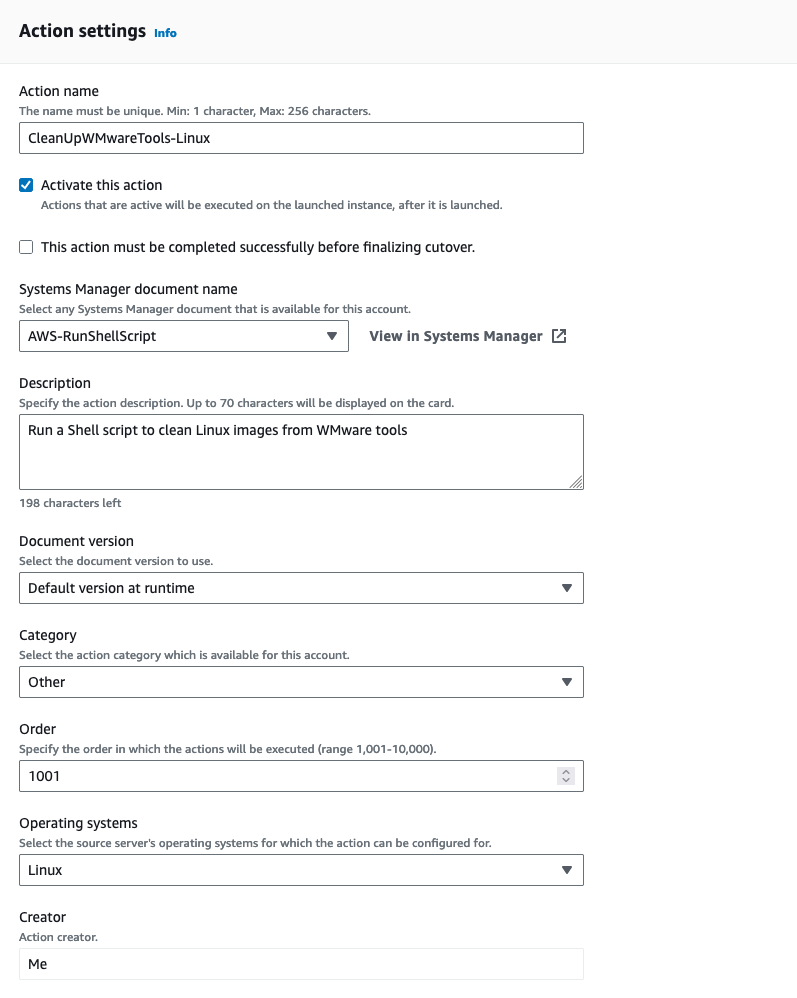
Figure 10: Shell script to remove VMware tools from replicated Linux launched instances.
Action parameters:
commands: rm -r ./VMware
workingDirectory (for RHEL 9): /usr/VMware
executionTimeout: 300
The Post-launch template (Figure 11) will show the two newly created actions. Make sure they are set as Active.
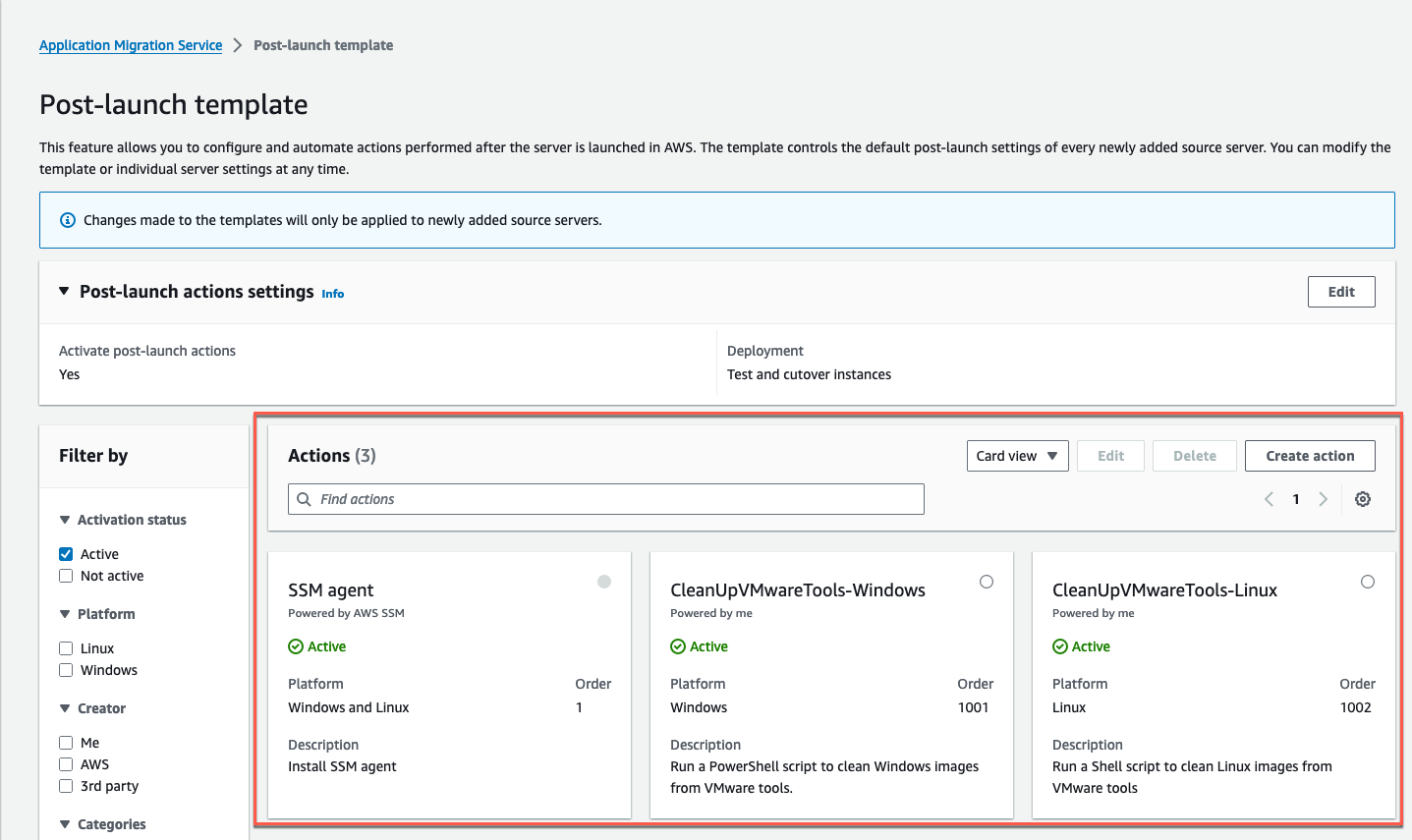
Figure 11: Verify that the SSM Agent installation and the two newly created post-launch actions are enabled.
Step 4 - Adding source servers and install agent on VMs
Each time you add a source server to Application Migration Service, its Replication settings, Launch settings, and Post-launch action settings are initialized based on the default templates.
You must add your source servers to the Application Migration Service console to migrate them into AWS. Source servers are added by installing the AWS Replication Agent on each individual server. Once your source servers have been added to the Application Migration Service, you can monitor and interact with them from the Source servers page. On this page, you can view all your source servers, monitor their migration lifecycle and data replication state, see the next step in the migration process for each server, and sort your servers by a variety of categories.
To add a Windows source server, select Add server on the Source servers page (Figure 12).
Figure 12: Add a source server by clicking on Add server.
Use the options below (Figure 13) to create the installer command, adding your IAM access key ID and IAM secret access key. Copy the resulting command and download the installer.
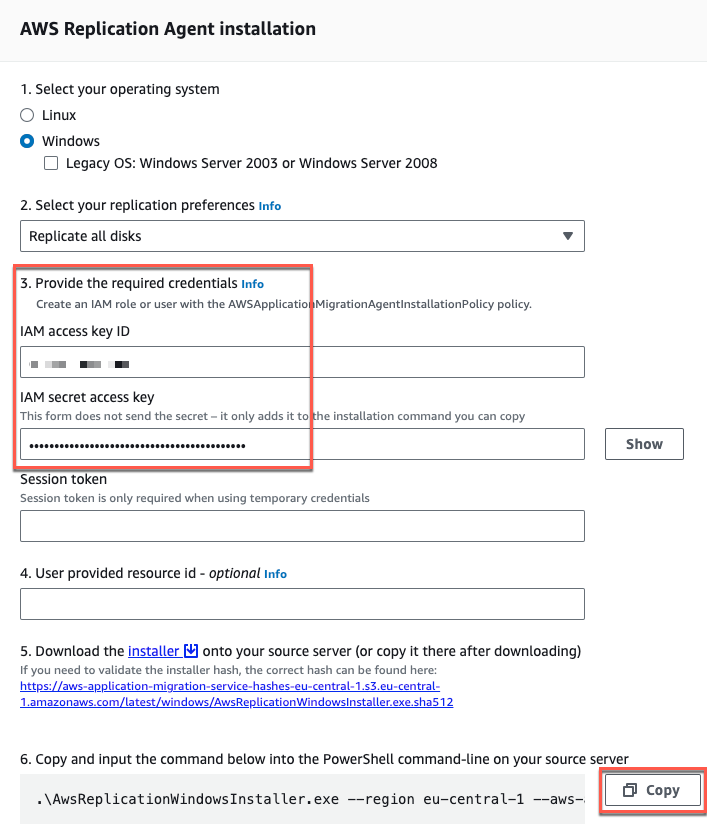
Figure 13: Generate the installer command line for the AWS Replication Agent.
Once the installer is downloaded, run the copied command in PowerShell. You need to run the agent installer file as an administrator on each Windows server (Figure 14).
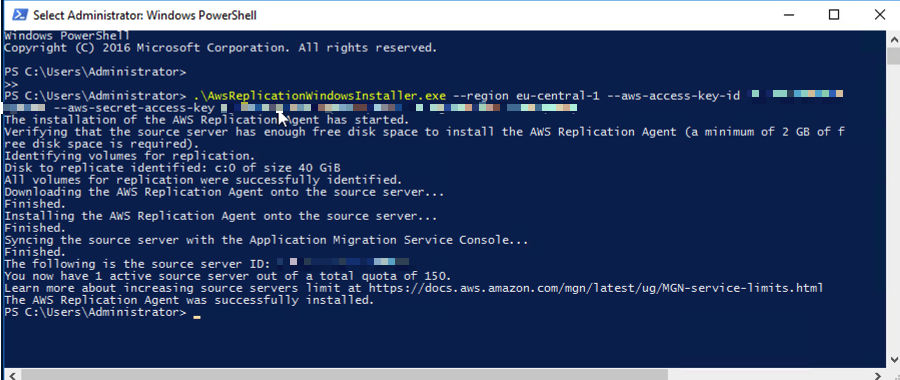
Figure 14: Run the agent installer command on your Windows source servers.
Note your hostname and go to the Application Migration Service console.
Once the AWS Replication Agent is installed, the server will be added to the Application Migration Service console under Source servers where it will begin the initial synchronization process (Figure 15).
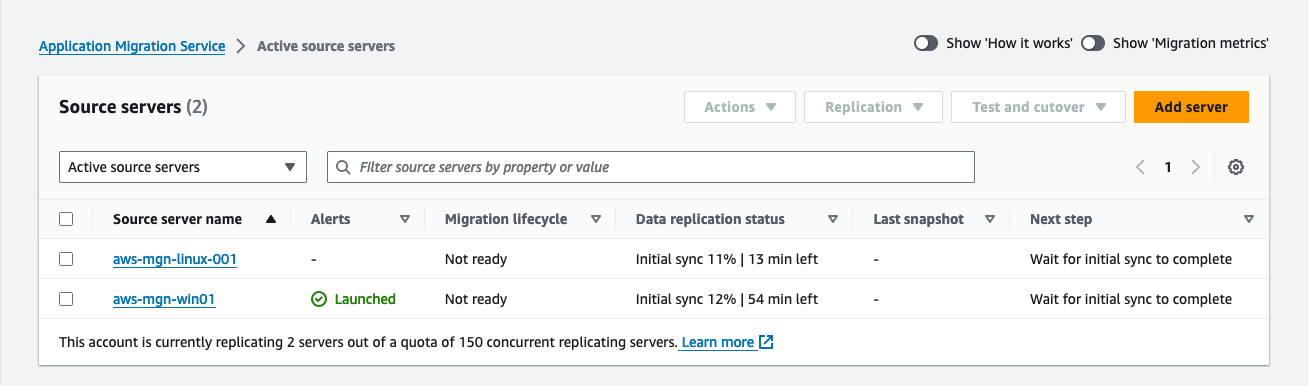
Figure 15: When the agent is connected to Application Migration Service, the source server will appear as active source servers.
Step 5 - Launching a test instance
Testing the migration of your source servers to AWS is essential before performing the cutover to ensure their proper functionality of the source server within the AWS environment.
Before launching a test instance, ensure that your source servers are ready for testing. Check for the following status on the Source servers page.
In the Migration lifecycle column, the server status should indicate Ready for testing.
In the Data replication status column, the server status should be Healthy.
In the Next step column, the server’s status should be Launch test instance.
To launch a test instance for one or more source servers, follow these steps:
Navigate to the Source servers page.
Select the checkbox next to each server you wish to test.
Select the Test and cutover menu.
Under Testing, select Launch test instances to initiate the launch of test instance(s) for the selected source server(s) (Figure 16).
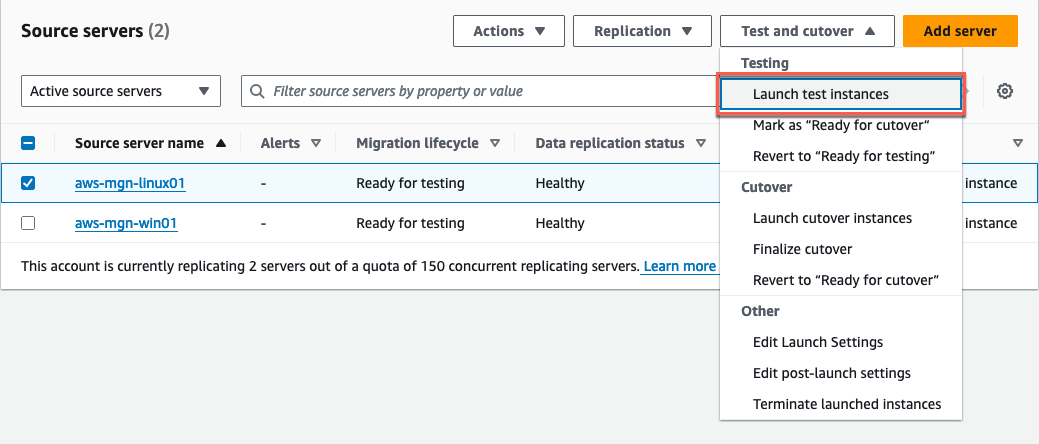
Figure 16: Select Launch test instances from the Test and cutover dropdown menu.
- Once the Launch test instances for X servers dialog appears, select Launch to commence the test (Figure 17).
Figure 17: Select Launch to start the tests.
- The AWS Application Migration Service console will indicate Launch job started when the test has started. Choose View job details on the dialog to view the specific job for the test launch in the Launch history tab (Figure 18).
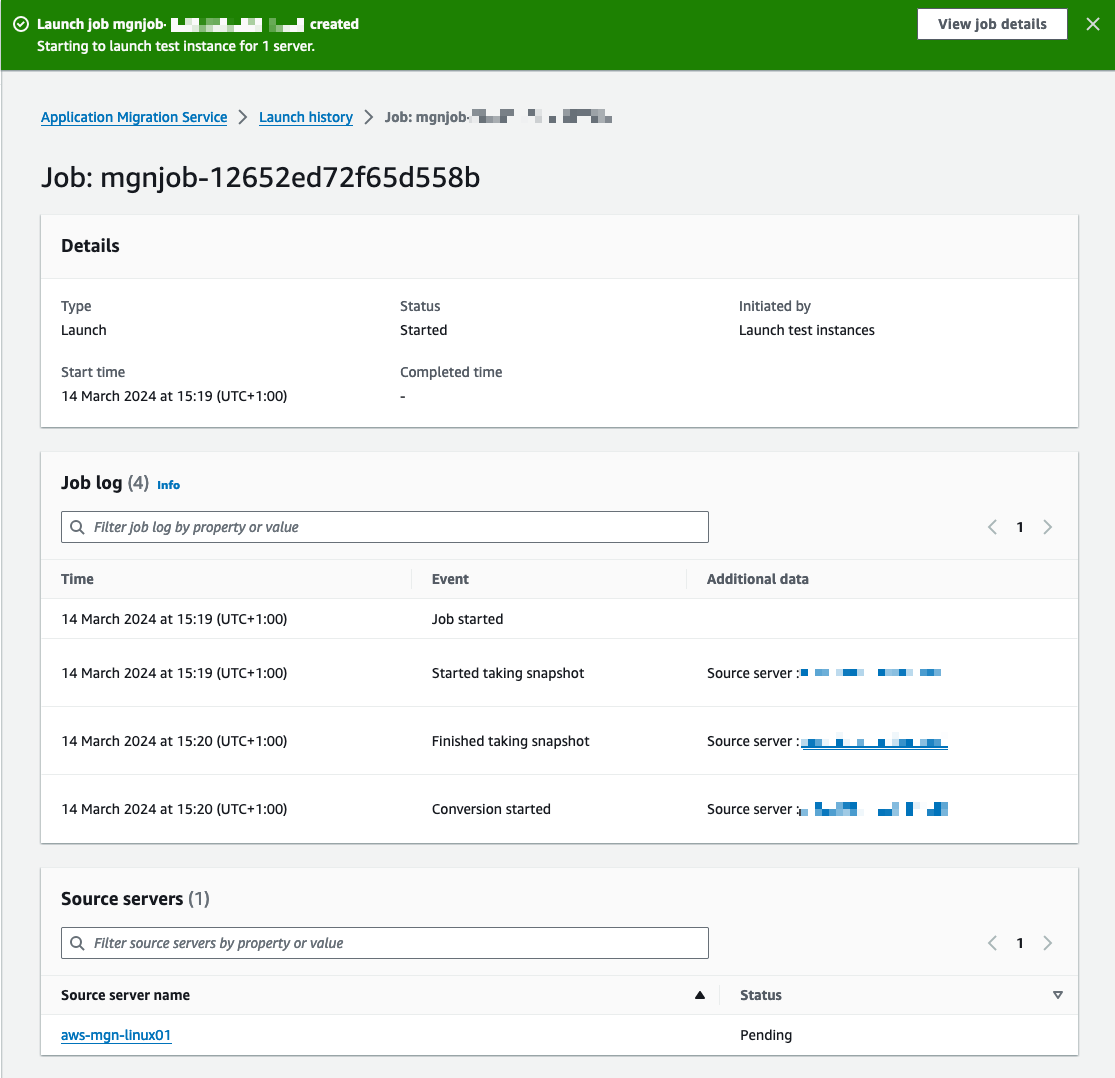
Figure 18: The banner shows that the job has started. You can select View job details if you need more information on that job.
- You can confirm the successful initiation of the test instance launch by observing various indicators on the Source servers page (Figure 19).
In the Alerts column, you will see a Launched status, signifying the launch of a test instance for this server.
In the Migration lifecycle column, you will see a status of Test in progress.
In the Next step column, it will show Complete testing and be marked as Ready for cutover.
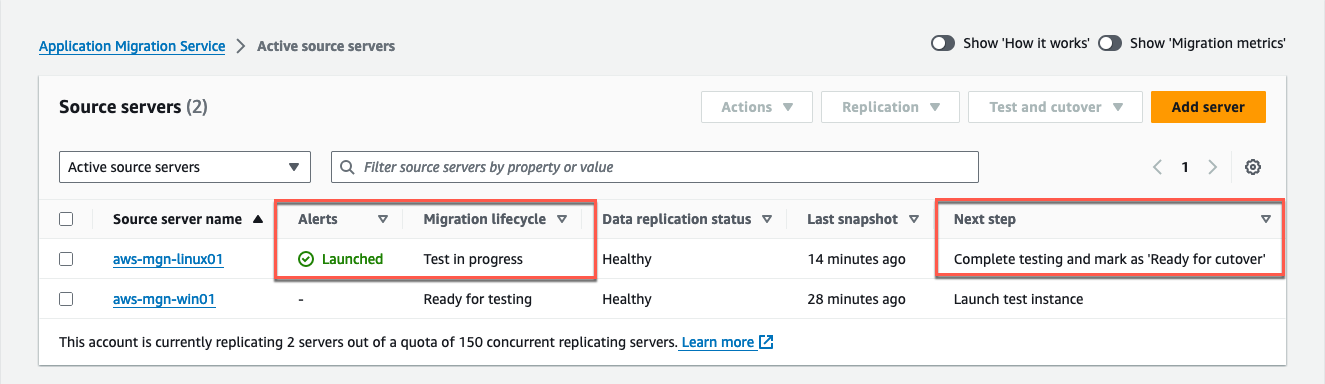
Figure 19: Mark the server as Ready for cutover when your tests are completed.
Once your test instances are launched, access the Amazon EC2 console and use SSH or RDP to connect to them. Alternatively, you can use AWS SSM Session Manager or AWS SSM Fleet Manager to log into those instances. This is done to verify their proper functionality, assess connectivity, and conduct acceptance tests for your application (Figure 20).
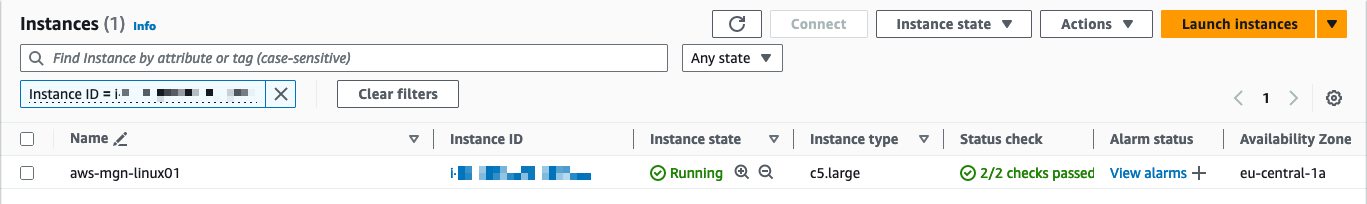
Figure 20: The test instance shows in the EC2 console.
When your testing is complete and you are prepared for the cutover phase, you can conclude the test. To do so, update the Migration lifecycle status of your source servers to Ready for cutover. It signifies the completion of all testing and the readiness for cutover. Eventually, conclude the lifecycle test in progress by selecting Terminate test launched instances.
Verify post-launch actions.
Select Source servers, and open the Post-launch settings tab.
For visibility on the actions that will be invoked, filter by active actions.
The following actions will be invoked (Figure 21).
SSM agent
CleanUpVMwareTools-Linux
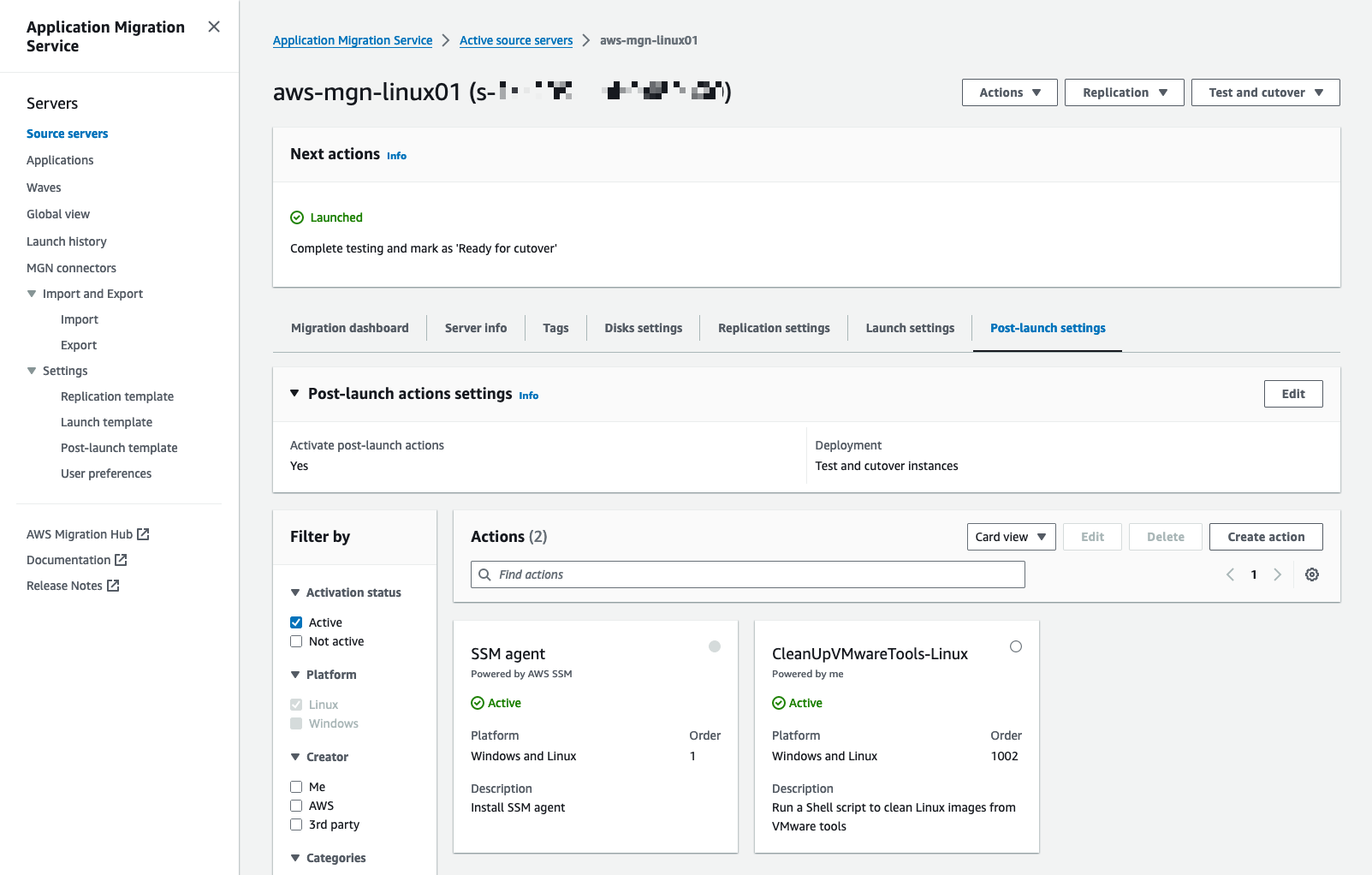
Figure 21: Validate post-launch actions to be executed.
When the instance is launched, the execution status of the SSM Agent installation and CleanUpVMWareTools can be tracked under the Migration dashboard tab (Figure 22).
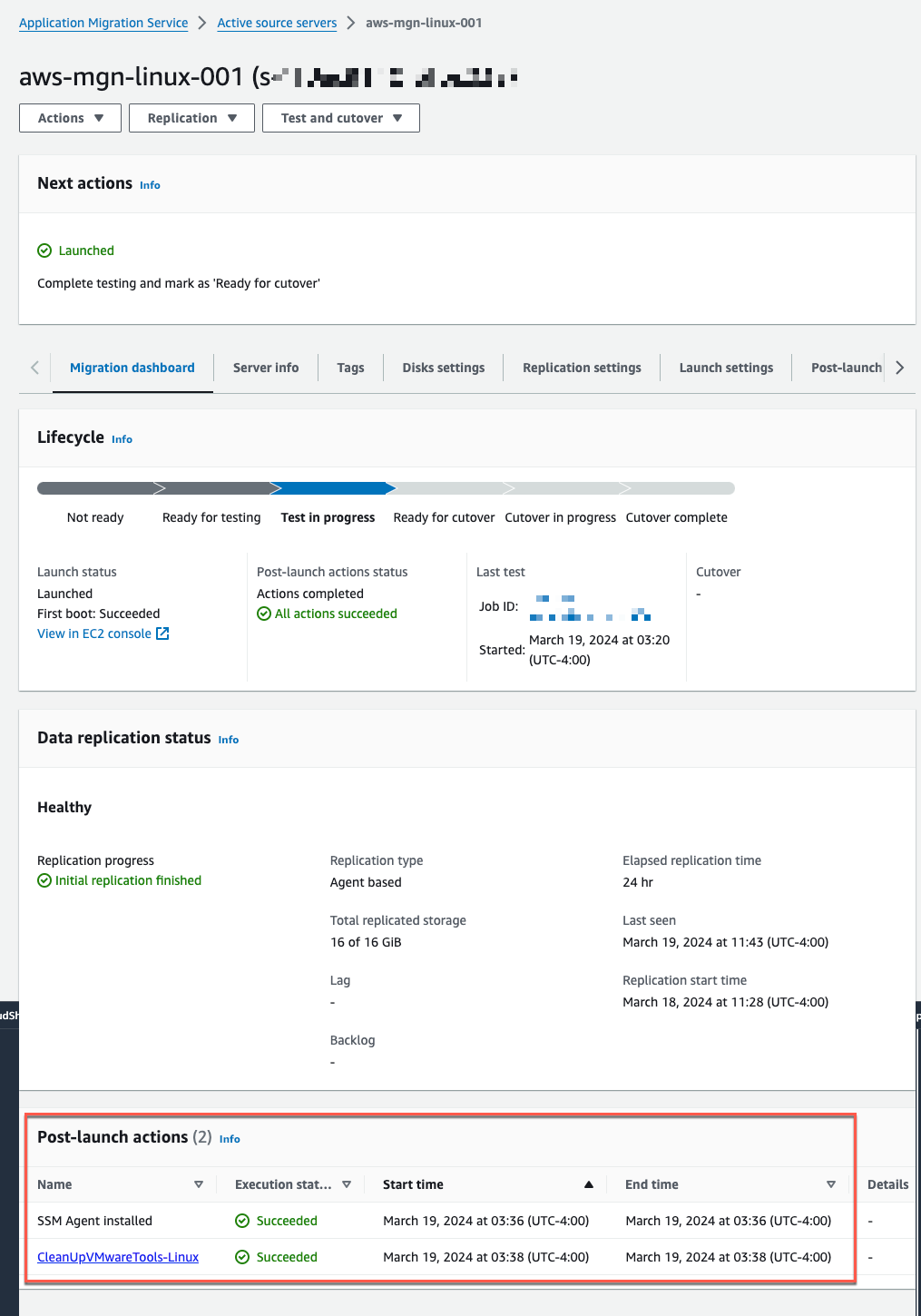
Figure 22: Note that all the actions completed successfully.
Step 6 - Launching a cutover instance
Select the checkbox next to each source server with a launched test instance for which you wish to conclude the test.
Select the Test and cutover menu (Figure 23).
Under the Testing section, select the option Ready for cutover.
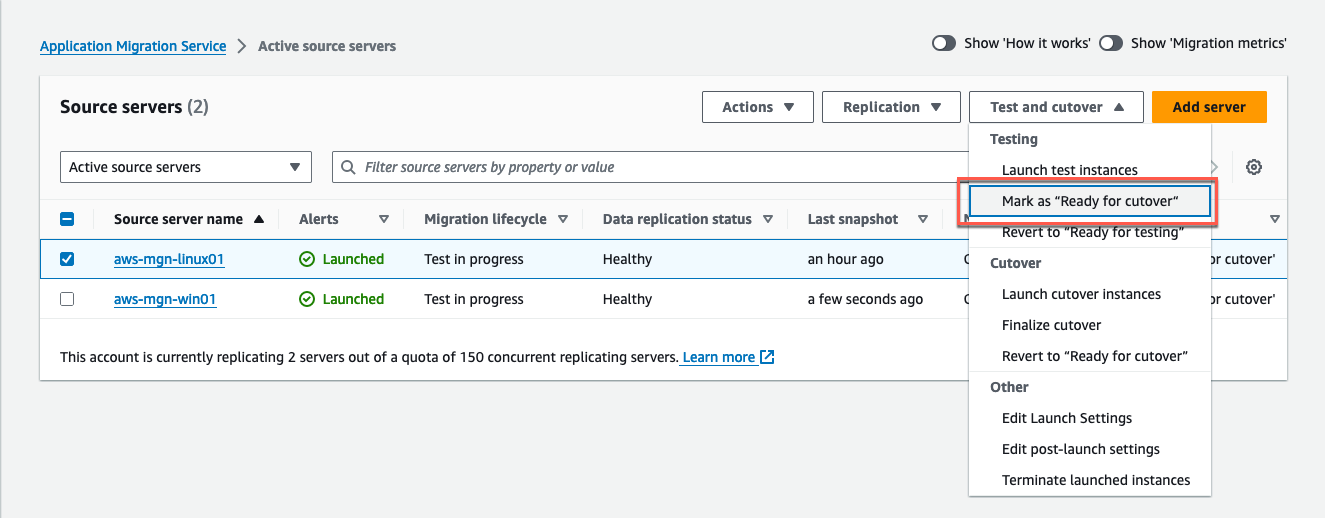
Figure 23: Mark as Ready for cutover to launch a cutover instance.
In the Mark X servers as “Ready for cutover” dialog, you can make a choice regarding the termination of the test instances. It is recommended that you terminate these instances because you will incur charges for them, even if they are no longer required. To proceed with termination, choose Yes, terminate launched instances (recommended) and then select Continue (Figure 24).
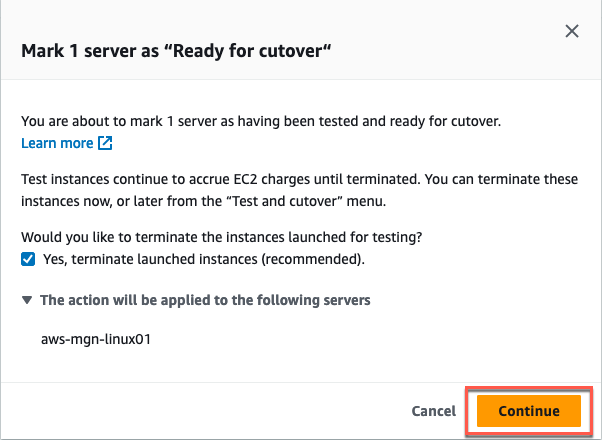
Figure 24: You can terminate the launched instance to reduce the costs (recommended), and select Continue.
The AWS Application Migration Service console will confirm that the servers were marked as ready for cutover (Figure 25).

Figure 25: The banner shows the summary, and you can select View job details if you need more information regarding the job.
Before proceeding with the launch of a cutover instance, confirm the readiness of your source servers for cutover by checking for the following status on the Source servers page (Figure 26).
Migration lifecycle status is Ready for cutover.
Data replication status is Healthy.
The next step shows Terminate launched instance; Launch cutover instance if you have not terminated your most recent test instance. Alternatively, Launch cutover instance if you have terminated the latest test instance.
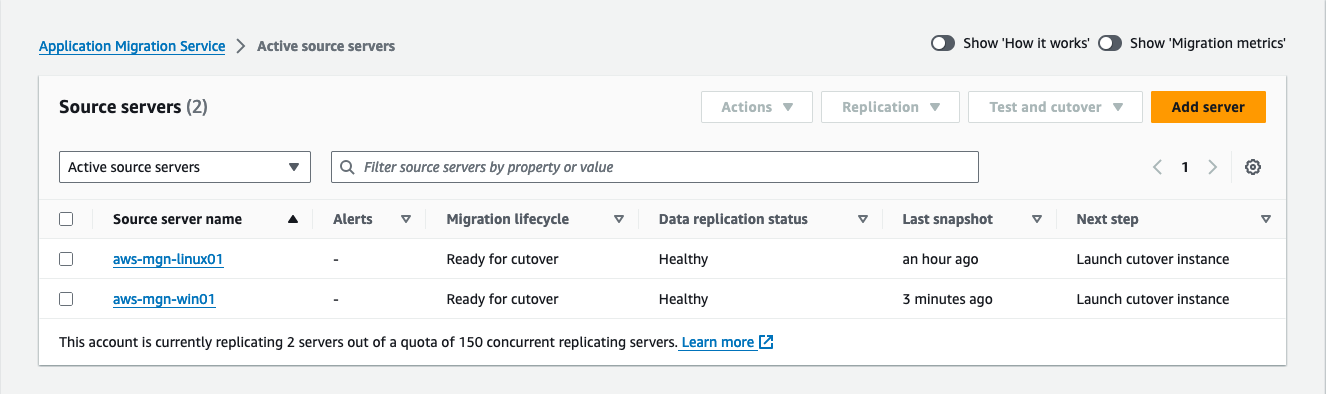
Figure 26: Validate that migration status is Ready for cutover, data replication status is Healthy.
To initiate a cutover instance for one or more source servers, follow these steps:
Visit the Source servers page, and select each server you wish to cutover.
Select the Test and cutover menu.
Under Cutover (Figure 27), select Launch cutover instances.
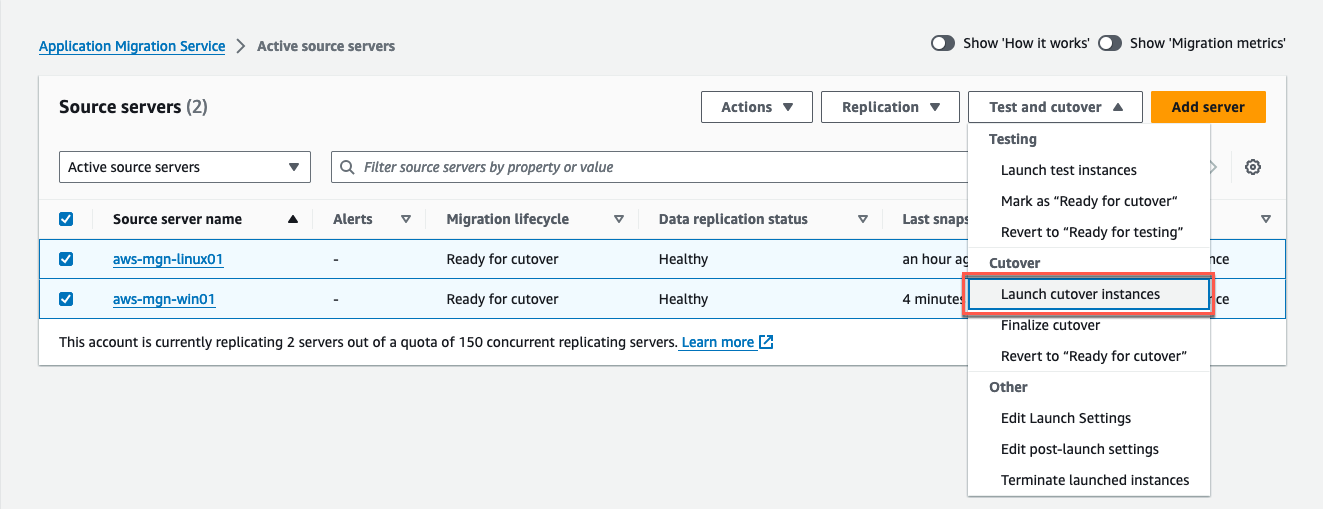
Figure 27: Select Launch the cutover instances in the test and cutover menu.
- A pop-up dialog appears showing the cutover instances with their respective names that will be launched. Confirm by selecting Launch (Figure 28).
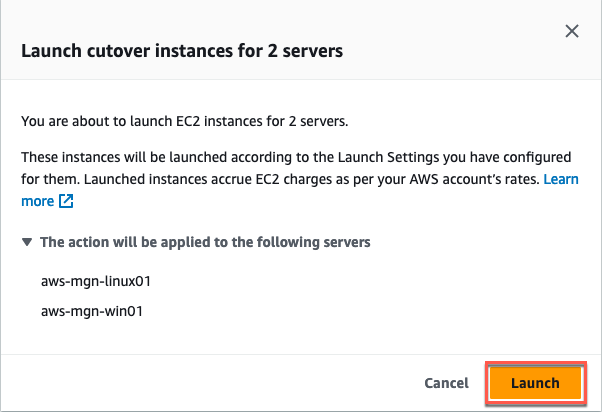
Figure 28: Review the listed servers before selecting Launch.
On the Source servers page (Figure 29), the Migration lifecycle column displays Cutover in progress and the Next step column indicates Finalize cutover.
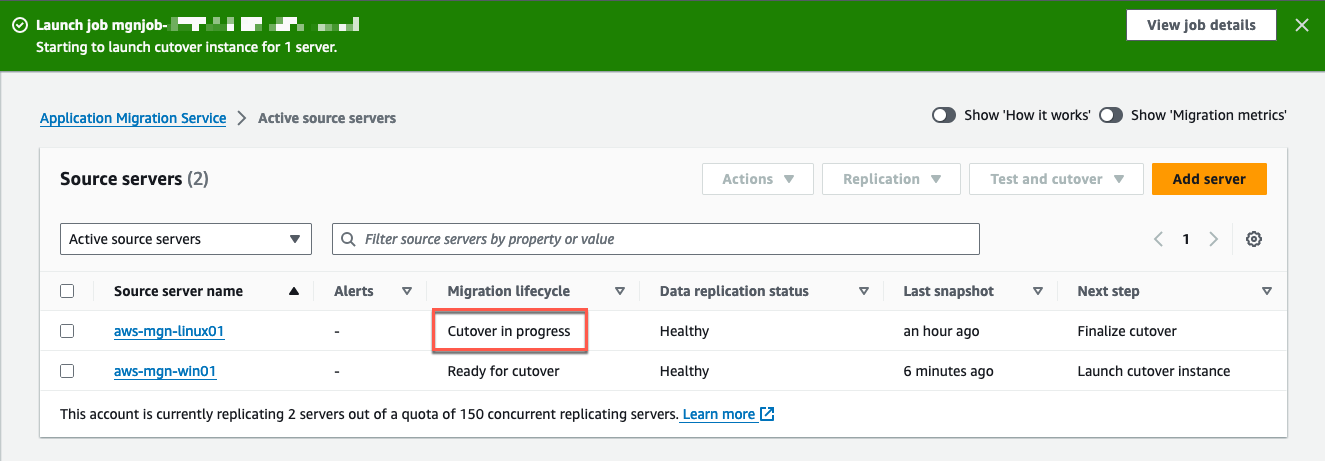
Figure 29: The migration lifecycle has changed from Ready for cutover to Cutover in progress.
Select your source server to view the job details (Figure 30).
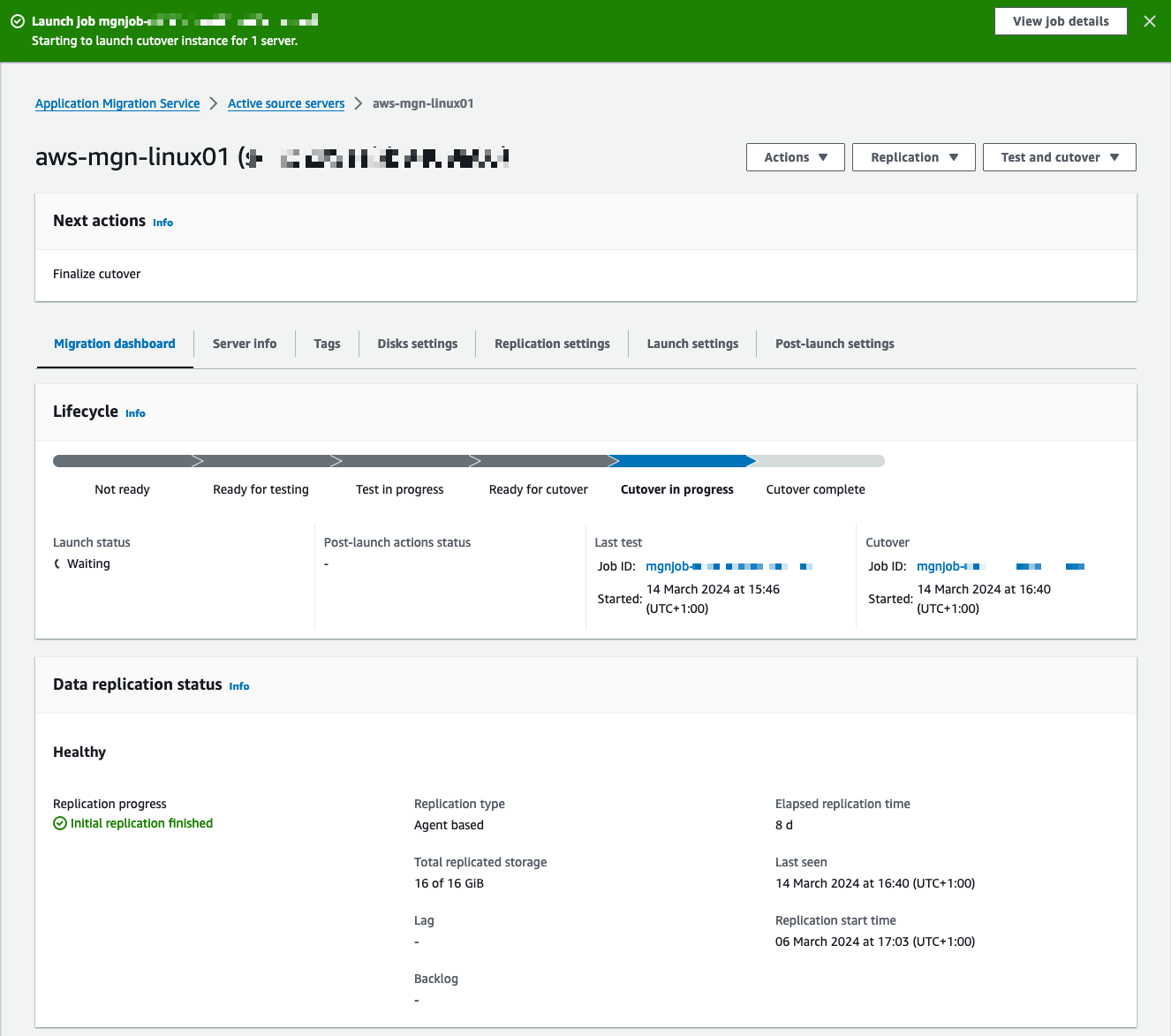
Figure 30: The current lifecycle is Cutover in progress, meaning the cutover instances are being launched.
After launching your cutover instances, connect to your cutover instances using SSH or RDP through the Amazon EC2 console. Alternatively, connect to the instance with Session Manager or Fleet Manager, capabilities of Systems Manager. This step is essential to verify their proper operation, confirm connectivity, and conduct acceptance tests for your application.
When you have completed your migration, finalize the cutover (Figure 31):
Choose each source server you wish to cut over.
Select: Finalize cutover.
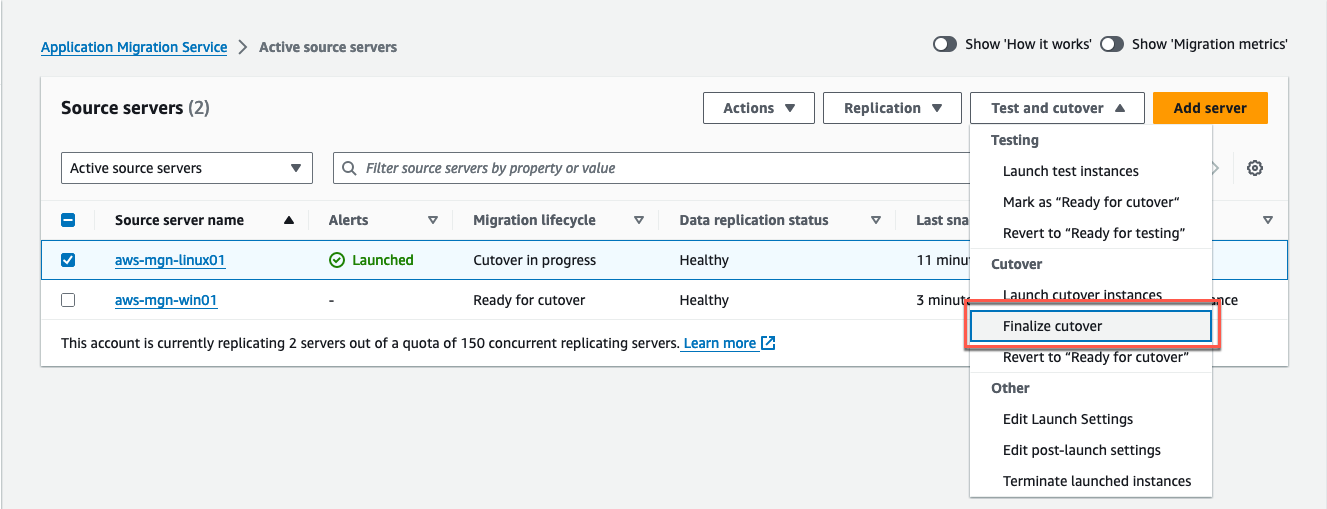
Figure 31: Switch to Finalize cutover to stop data replication.
In the Finalize cutover for X servers dialog, select: Finalize to start the cutover (Figure 32).
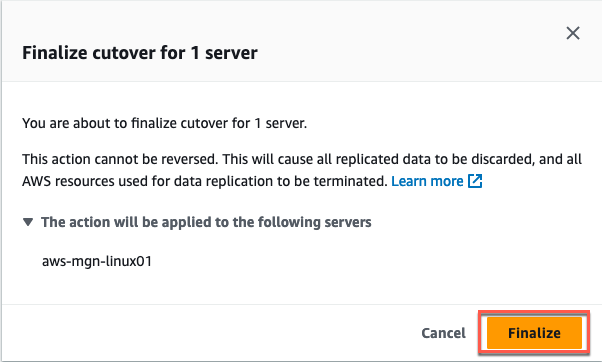
Figure 32: Review the listed server(s) and select Finalize.
This action will update the Migration lifecycle status of your source servers to: Cutover complete, signifying a successful cutover and migration. It will also halt data replication and discard the associated AWS EBS volumes and Amazon EC2 replication servers. The Application Migration Service console will indicate Cutover finalized when the cutover has completed successfully (Figure 33).
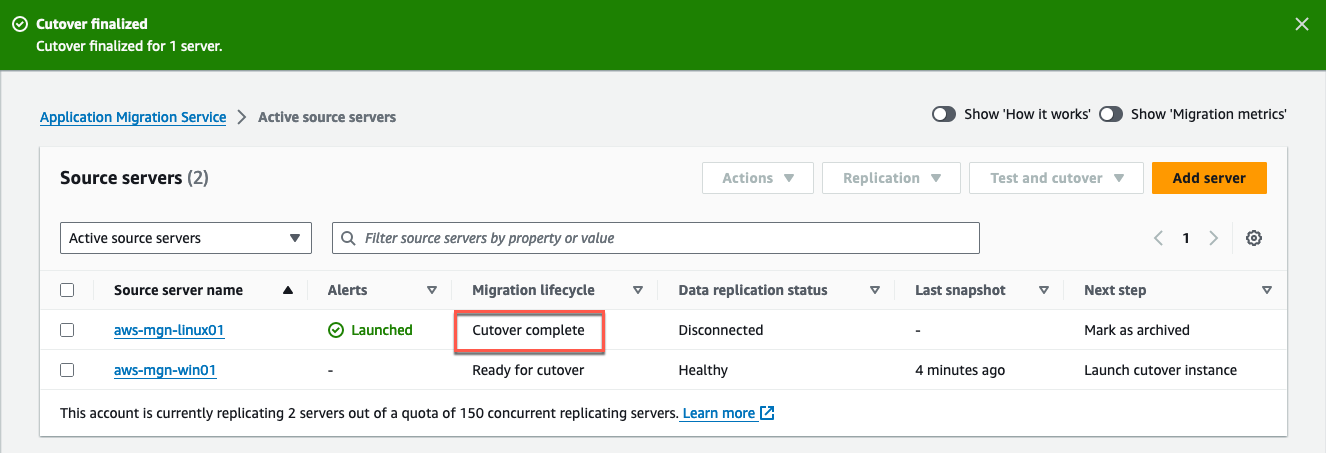
Figure 33: The Migration lifecycle shows Cutover complete.
Cleanup
To avoid ongoing charges, ensure to clean up relevant resources, including:
Clean up Amazon EC2 instances
Disconnect any Application Migration Service source servers
Remove attached EBS volumes to the EC2 instances associated with your testing
Delete VPC endpoints
Conclusion
This implementation guide reviews the series of steps for a seamless on-demand migration of a VMware VM to Amazon EC2. The main benefit of this process is automation, which significantly reduces human errors and accelerates the migration. The post-launch actions clean up images from VMware tools. Application Migration Service remains cost-effective, making it an ideal solution for migrations regardless if the VMware environment is on-premises, in another cloud provider, or in VMware Cloud on AWS.
For additional resources, see the following topics in the Application Migration Service User Guide:
Contributors
Simon Vaillancourt
Philippe Wanner
Notices
Customers are responsible for making their own independent assessment of the information in this document. This document: (a) is for informational purposes only, (b) represents AWS current product offerings and practices, which are subject to change without notice, and (c) does not create any commitments or assurances from AWS and its affiliates, suppliers or licensors. AWS products or services are provided “as is” without warranties, representations, or conditions of any kind, whether express or implied. AWS responsibilities and liabilities to its customers are controlled by AWS agreements, and this document is not part of, nor does it modify, any agreement between AWS and its customers.