Guidance for Security Compliance and Patching of VMware and Amazon EC2 Workloads
Summary: This implementation guide provides an overview of Guidance for Security Compliance and Patching of VMware and Amazon EC2 Workloads, its reference architecture and components, considerations for planning the deployment, and configuration steps for deploying this Guidance to Amazon Web Services (AWS). This guide is intended for solution architects, business decision makers, DevOps engineers, data scientists, and cloud professionals who want to implement Guidance for Security Compliance and Patching of VMware and Amazon EC2 Workloads in their environment.
Overview
This document outlines the use cases and solution for security compliance and patching of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) and VMware based workloads running on VMware Cloud on AWS in addition to on-premises vSphere VMs.
Features and benefits
The AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF) leverages AWS experience and best practices to help you digitally transform and accelerate your business outcomes through innovative use of AWS. This solution architecture maps back to the Operations Perspective and Security Perspective of the AWS CAF. We are focused on patch management and infrastructure protection capabilities and the use cases for which these perspectives solve.
Hybrid environments bring operational challenges that are not typically present in homogenous, on-premises environments. Maintaining patch levels across multiple operating systems with the added complexity of doing this across cloud and on-premises infrastructure forces systems administrators to connect to multiple tools for management of security and compliance, which may leave gaps in observability. Leveraging a set of purpose-built services that provide coverage in AWS, VMware Cloud on AW,S and on-premises delivers centralized visibility and minimizes operational overhead.
Use cases
This implementation guide is relevant to customers who would like to provide a centralized patching and compliance management solution for all their VMware virtual machines (VMs) on-premises, in their VMware Cloud on AWS software defined data centers and their Amazon EC2 instances within AWS. By deploying this Guidance, you will gain 1) visibility of compliance, 2) vulnerabilities and security baselines across differing instance and VM types, and 3) the ability to control and remediate these vulnerabilities and security baseline levels from a centralized administrative console.
Architecture Overview
This section provides a reference implementation architecture diagram for the components deployed with this Guidance.
The Guidance consists of AWS Security Hub, VMware Cloud on AWS (VMware software-defined data center [SDDC] stack comprising of vSphere, ESXi, NSX-T and VSAN), and Amazon EC2 instances or on-premises server instances as the target environment to manage. The Guidance uses AWS Systems Manager integrated with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles, virtual private cloud (VPC), and firewalls, to provide a secure maintenance and compliance system for multiple instance patching and control.
Rather than dealing with different products to patch and maintain different types of servers and VM instances, this Guidance can help customers implement patching and compliance management from a “single pane of glass” or a single, centralized hub.
Architecture diagram
Figure 1 below shows the reference architecture for Guidance for Security Compliance and Patching of VMware and Amazon EC2 Workloads.
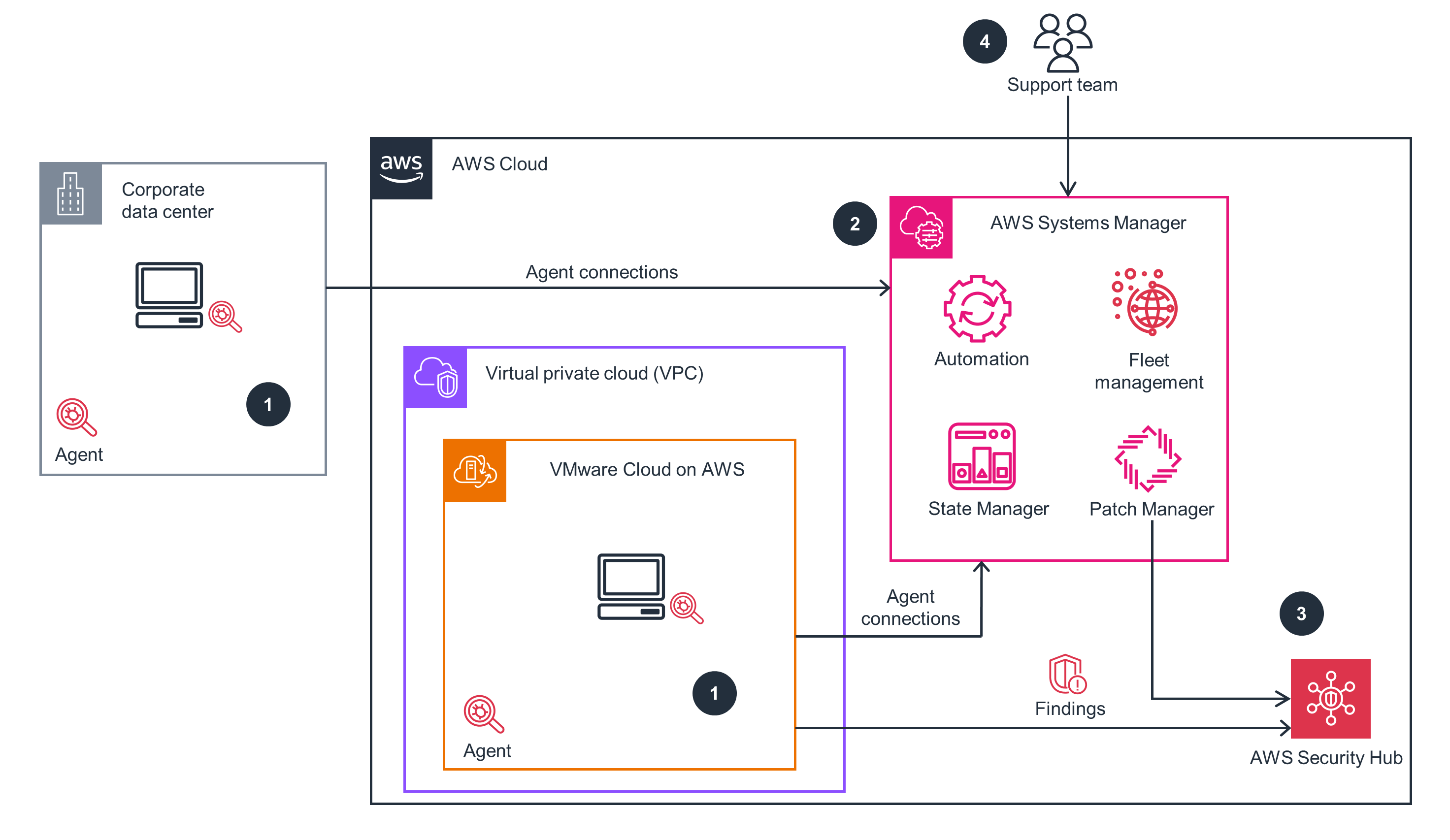
Figure 1: Guidance for Security Compliance and Patching of VMware and Amazon EC2 Workloads reference architecture
Solution function
With Security Hub, you can enable checks for standard best practices, such as the following:
- AWS Foundational Security Best Practices
- Center for Internet Security (CIS) AWS Foundations Benchmark
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
Each of these standards has predefined controls. Security Hub checks for the control in a given AWS account, reports the findings, and sends all findings to Amazon EventBridge by default.
By using the integration between Patch Manager, a capability of AWS Systems Manager, and Security Hub, you can send findings about noncompliant nodes from Patch Manager to Security Hub. A finding is the observable record of a security check or security-related detection. Security Hub can then include those patch-related findings in its analysis of your security posture.
At this time, Security Hub reports the resource type of all managed nodes as “EC2 Instance.” This includes on-premises servers and VMs that you have registered for use with Systems Manager.
You can use Systems Manager to manage both EC2 instances and a number of non-EC2 machine types in a hybrid and multi-cloud environment.
This Guidance requires an inventory of and data collection from the workloads. Systems Manager uses an agent (SSM Agent) that is pre-installed in many of the available AWS machine image files for Amazon EC2. It is necessary to install the SSM Agent into the nodes located on-premises or in VMware Cloud on AWS that you want to manage.
SSM Agent requires communication with the AWS API, and this communication uses standard HTTPS ports. Because the SSM Agent always starts the communication, allowing any inbound rules is not necessary (egress ports 443 and 80 on 0.0.0.0/0 with tcp). If SSM Agent can’t connect with service endpoints, then the SSM Agent will fail. SSM Agent must make an outbound connection with the following Systems Manager service API calls on port 443:
- SSM endpoint: ssm.REGION.amazonaws.com
- EC2 messaging endpoint: ec2messages.REGION.amazonaws.com
- SSM messaging endpoint: ssmmessages.REGION.amazonaws.com
SSM Agent uses the Region information that the instance metadata service retrieves to replace the REGION value in these endpoints.
When SSM Agent can’t reach the metadata service, it also can’t locate the AWS Region information, IAM role, or instance ID from that service. In this case, an error message will appear in the SSM Agent logs similar to the following:
INFO- Failed to fetch instance ID. Data from vault is empty. RequestError: send request failed caused by: Get http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id
After configuring your hybrid and multi-cloud environment for Systems Manager, you can do the following:
- Create a consistent and secure way to remotely manage your hybrid and multi-cloud workloads from one location using the same tools or scripts.
- Centralize access control for actions that can be performed on your machines by using IAM.
- Centralize auditing of the operations performed on your machines by viewing the API activity recorded in AWS CloudTrail.
- For information about using CloudTrail to monitor Systems Manager actions, review Logging AWS Systems Manager API calls with AWS CloudTrail.
- Centralize monitoring by configuring Amazon EventBridge and Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) to send notifications about service execution success.
- For information about using EventBridge to monitor Systems Manager events, review Monitoring Systems Manager events with Amazon EventBridge
Following installation of the SSM Agent, use the AWS Systems Manager Inventory tool to collect metadata about applications, files, components, patches, and more from your managed nodes.
You can store this metadata in a central Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket, and then use built-in tools to query the data and quickly determine which nodes are running the software and configurations required by your software policy and which nodes need to be updated. You can configure Inventory on all of your managed nodes by using a one-click procedure. You can also configure and view inventory data from multiple AWS Regions and AWS accounts. To get started with Inventory, open the AWS Systems Manager console. In the navigation pane, choose Inventory.
The data collected from the workloads is analyzed by Systems Manager against patching baselines. The findings of System Manager are forwarded to Security Hub.
Use Patch Manager to automate the process of patching your managed nodes with both security related and other types of updates. You can use Patch Manager to apply patches for both operating systems and applications. (On Windows Server, application support is limited to updates for applications released by Microsoft.)
Patch Manager provides predefined patch baselines for each of the operating systems supported by Patch Manager. You can use these baselines as they are currently configured (without customization), or you can create your own custom patch baselines.
Custom patch baselines allow greater control over which patches are approved or rejected for your environment. Also, the predefined baselines assign a compliance level of Unspecified to all patches installed using those baselines. For compliance values to be assigned, you can create a copy of a predefined baseline and specify the compliance values you want to assign to patches.
This capability allows you to scan managed nodes for missing patches and apply missing patches either individually or to large groups of managed nodes by using tags. Patch Manager uses patch baselines, which can include rules for auto-approving patches within days of their release, and a list of approved and rejected patches. You can install security patches on a regular basis by scheduling patching to run as a Systems Manager maintenance window task, or you can patch your managed nodes on demand at any time.
Use Compliance, a capability of Systems Manager, to scan your fleet of managed nodes for patch compliance and configuration inconsistencies. You can collect and aggregate data from multiple AWS accounts and AWS Regions and then drill down into specific resources that aren’t compliant.
By default, Compliance displays compliance data about Patch Manager patching and State Manager (also a capability of Systems Manager) associations.
You can also customize the service and create your own compliance types based on your IT or business requirements.
The standard patching process for VMware Cloud on AWS and on-premises instances consists of two steps:
- You configure your VMware Cloud on AWS and on-premises servers to be managed by Systems Manager. For the details of this process, review Setting up Systems Manager for hybrid environments in the Systems Manager documentation.
- You configure the appropriate Patch Group and Maintenance Window tags for these on-premises managed instances by using the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) add-tags-to-resource command.
This approach requires either the application team or the cloud team to manually run the AWS CLI commands whenever they want to perform changes to the patch groups or maintenance windows.
Automated patching for mutable instances in the hybrid cloud using AWS Systems Manager prescriptive guidance is available if you prefer to automate this process.
Patch Manager is one of the Systems Manager capabilities that sends findings to Security Hub. After you perform a patching operation by running an SSM document (AWS-RunPatchBaseline, AWS-RunPatchBaselineAssociation, or AWS-RunPatchBaselineWithHooks, the patching information is sent to Inventory, a capability of Systems Manager, or Compliance, or both. After Inventory, Compliance, or both receive the data, Patch Manager receives a notification. Then, Patch Manager evaluates the data for accuracy, formatting, and compliance. If all conditions are met, Patch Manager forwards the data to Security Hub.
Security Hub automatically sends all new findings and all updates to existing findings to EventBridge as EventBridge events. You can also create custom actions that allow you to send selected findings and insight results to EventBridge.
You then configure EventBridge rules to respond to each type of event.
EventBridge uses a defined JSON-based structure for events and helps you create rules that are applied across the entire event body to select events to forward to a target. EventBridge currently supports over 20 AWS services as targets, including AWS Lambda, Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS), Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS), Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, and Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose.
Using Amazon CloudWatch logs rules, it is possible to invoke orchestration of remediation playbooks in Lambda or AWS Step Functions.
Security Hub cross-Region aggregation
Security Hub includes support for cross-Region aggregation, and when this is enabled, Security Hub aggregates new findings, insights, control compliance statuses, and security scores from the linked Regions to the aggregation Region.
Security Hub also replicates updates to this data between the linked Regions and the aggregation Region. Updates that occur in a linked Region are replicated to the aggregation Region. Updates that occur in the aggregation Region are replicated back to the original linked Region.
Security Hub service integrations
Security Hub is integrated with many additional AWS services, and this enables you to easily monitor your AWS native infrastructure with little to no additional effort.
With the exception of sensitive data findings from Amazon Macie, you are automatically opted in to all other AWS service integrations with Security Hub. If you’ve turned on Security Hub and the other service, no other step is needed to activate the integration between the two services.
AWS Services in this Guidance
This Guidance includes the AWS services listed below.
AWS Security Hub
Security Hub is a cloud security posture management service that performs security best practice checks, aggregates alerts, and enables automated remediation.
AWS Systems Manager
Systems Manager is the operations hub for your AWS applications and resources and a secure end-to-end management service for hybrid and multi-cloud environments that enable secure operations at scale.
Using Systems Manager Hybrid Activations, you can manage resources irrespective of where they are hosted. You can securely initiate remote shell connections, automate patch management, and monitor critical metrics. You’re able to gain visibility into networking information and application installations using a single console.
Patch Manager
Patch management is vital in maintaining a secure and compliant environment. Patch Manager helps you monitor, select, and deploy operating system and software patches automatically. This can happen across compute running on Amazon EC2, VMware on-premises, or VMware Cloud on AWS instances.
State Manager
State Manager is a secure and scalable configuration management service that automates the process of keeping your managed Amazon EC2 or on-premises instances and other AWS resources in a state that you define.
SSM Agent
SSM Agent is an Amazon software that runs on EC2 instances, edge devices, on-premises servers, and VMs. SSM Agent makes it possible for Systems Manager to update, manage, and configure these resources. The SSM Agent processes requests from the Systems Manager service in the AWS Cloud and then runs them as specified in the request. SSM Agent then sends status and execution information back to Systems Manager by using the Amazon Message Delivery Service (service prefix: ec2messages).
Amazon Detective
Amazon Detective simplifies the investigative process and helps security teams conduct faster and more effective investigations. With the Detective prebuilt data aggregations, summaries, and context, you can quickly analyze and determine the nature and extent of possible security issues.
Amazon Inspector
Amazon Inspector is an automated vulnerability management service that continually scans AWS workloads for software vulnerabilities and unintended network exposure.
- An agent is required to perform scans, and most operating systems are supported (at least most Linux and Windows Operating Systems).
- An EventBridge rule uses a cron expression to self-initiate on a specific schedule and initiates Inspector.
Amazon CloudWatch
CloudWatch collects and visualizes real-time logs, metrics, and event data in automated dashboards to streamline your infrastructure and application maintenance.
CloudWatch Agent
CloudWatch agent enables you to do the following:
- Collect internal system-level metrics from EC2 instances across operating systems. The metrics can include in-guest metrics in addition to the metrics for EC2 instances. The additional metrics that can be collected are listed in Metrics collected by the CloudWatch agent.
- Collect system-level metrics from on-premises servers. These can include servers in a hybrid environment and servers not managed by AWS.
- Retrieve custom metrics from your applications or services using the StatsD and Collectd protocols. StatsD is supported on both Linux servers and servers running Windows Server. Collectd is supported only on Linux servers.
- Collect logs from EC2 instances and on-premises servers, running either Linux or Windows Server.
- Use Systems Manager to install the CloudWatch agent.
Collecting metrics and logs from Amazon EC2 instances and on-premises servers with the CloudWatch agent is explained in the CloudWatch documentation.
AWS Config
AWS Config continually assesses, audits, and evaluates the configurations and relationships of your AWS resources on AWS on-premises, and on other clouds.
AWS Config provides a visual dashboard to help you quickly spot noncompliant resources and take appropriate action. IT administrators, security experts, and compliance officers can view a shared view of your resources’ compliance posture.
AWS Config helps you record software configuration changes within your EC2 instances and servers running on-premises in addition to servers and VMs in environments provided by other cloud providers. With AWS Config, you gain visibility into operating system (OS) configurations, system-level updates, installed applications, network configuration and more.
If you have configured AWS Config to record all resource types, then third-party resources that are managed (created, updated, or deleted) through AWS CloudFormation are automatically tracked in AWS Config as configuration items.
AWS CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation lets you model, provision, and manage AWS and third-party resources by treating infrastructure as code. The CloudFormation AWS::SSM::Association resource creates a Systems Manager, State Manager association for your managed instances. A State Manager association defines the state that you want to maintain on your instances. For example, an association can specify that anti-virus software must be installed and running on your instances or that certain ports must be closed. For static targets, the association specifies a schedule for when the configuration is reapplied. For dynamic targets, such as an AWS Resource Groups or an AWS Auto Scaling Group, State Manager applies the configuration when new instances are added to the group. The association also specifies actions to take when applying the configuration. For example, an association for anti-virus software might run once a day. If the software is not installed, then State Manager installs it. If the software is installed, but the service is not running, then the association might instruct State Manager to start the service.
Amazon EventBridge
EventBridge is a serverless service that uses events to connect application components together, making it easier for you to build scalable event-driven applications. Use it to route events from sources such as home-grown applications, AWS services, and third-party software to consumer applications across your organization. EventBridge provides a simple and consistent way to ingest, filter, transform, and deliver events so you can build new applications quickly.
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams
Kinesis Data Streams is a serverless streaming data service that makes it easy to capture, process, and store data streams at any scale.
AWS Lambda
Lambda is a serverless, event-driven compute service that lets you run code for virtually any type of application or backend service without provisioning or managing servers. You can invoke Lambda from over 200 AWS services and software as a service (SaaS) applications, and only pay for what you use.
AWS Lambda Syslog Parser + ASFF Transformation
Most operating systems, firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are capable of emitting events through Syslog. The purpose of this is to provide a sample AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK) project to create all the necessary resources for you to receive streaming Syslog events, parse and transform these events to AWS Security Finding Format (ASFF), and lastly, ingest these events as findings in Security Hub.
fluentd
fluentd is an open-source data collector, which lets you unify the data collection and consumption for a better use and understanding of data. The fluentd Container Solution packaged by Bitnami is available in AWS Marketplace.
VMware Aria Operations for Logs
VMware Aria Operations for Logs Service collects and analyzes logs generated in your SDDC.
A trial version of the VMware Aria Operations for Logs service is enabled by default in a new SDDC. The trial period begins when a user in your organization activates the VMware Aria Operations for Logs service, and it expires in thirty days. After the trial period, you can choose to subscribe to this service or continue to use a subset of service features at no additional cost.
Related Resources
We recommend reviewing the following related resources:
- AWS Cloud Operations & Migrations Blog: Review the AWS blog: Use AWS Systems Manager for VMware Cloud on AWS (VMC) operations management
- Compliance Support: Access information and support related to AWS compliance.
- AWS Artifact: AWS Artifact offers a number of documents for downloading. Getting started is simple for new and existing AWS accounts. Use this Getting Started tutorial to start downloading documents. For a more detailed guide, refer to the AWS Artifact documentation.
- Sales Support: Reach an AWS sales representative at the Contact Us page.
- VMware Cloud on AWS Support: Contact a VMware Cloud on AWS representative at the Contact Us page.
For more information, contact your AWS specialist solutions architect (SA) or account representative.
Notices
Customers are responsible for making their own independent assessment of the information in this document. This document: (a) is for informational purposes only, (b) represents AWS current product offerings and practices, which are subject to change without notice, and (c) does not create any commitments or assurances from AWS and its affiliates, suppliers or licensors. AWS products or services are provided “as is” without warranties, representations, or conditions of any kind, whether express or implied. AWS responsibilities and liabilities to its customers are controlled by AWS agreements, and this document is not part of, nor does it modify, any agreement between AWS and its customers.